What is IRC Section 409A?
Do I Need a Valuation of my Private Company’s Shares in Order to Issue Options?
An IRC Section 409A Valuation is an independent determination of the Fair Market Value of employee stock options issued by a private company. The Internal Revenue Service established this requirement in 2004 in response to industry practices that resulted in underpricing of employee stock options. The IRS regulations require that the option exercise price is at least equal to the Fair Market Value of the underlying shares.
A private company must complete the valuation process before granting options. The valuation report remains valid for 12 months following its effective date (provided no material change occurs during this period). Regulations define a subsequent external financing as a material change and this event triggers a 409A “refresh”.
From a business perspective, these IRS regulations led to the pervasive adoption of valuation services by private companies seeking 409A compliance. If the IRS decides a company didn’t comply with IRC Section 409A, this will result in severe tax consequences. The IRS will impose these taxes on the company and on the employees receiving options.
A private company can eliminate this risk by using a qualified independent valuation provider to set the FMV of the option exercise price. This creates a presumption that the business has undertaken good faith compliance with the 409A regulations. Reliance upon this Safe Harbor has become a standard governance practice for startup and venture-backed companies.
When do I need to get a 409A Valuation?
Most startup companies begin to use external valuation providers after closing an initial round of financing. This financing transaction establishes a relevant data point for the FMV of the company’s shares. External financing transactions can lead to 409A valuations because they precede the creation of new employee stock option pools. We have also seen a growing trend of bootstrapped company owners obtaining a 409A Valuation to demonstrate good governance practices to management and employees.
Since the IRS issued IRC 409A regulations in 2004, the body of literature and accepted practices for private company stock option valuations has evolved. The AICPA issued a Practice Guide on the Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation in 2004 (updated in 2013). This resource defines the valuation methods applicable to 409A valuation analyses. These valuation methods differ in a number of respects from those applicable to a standard business valuation. As a result, most companies select a valuation provider who specializes in providing IRC 409A Valuations.
How is the Value of the Common Shares Determined?
The first step in determining FMV of the shares is to determine the Enterprise Value of the company. This part of the analysis relies upon methods similar to those used in a standard business valuation. These can include valuation methods based on the assets, income and market value of the subject company. The valuation firm should consider industry-specific valuation methods and identify comparable publicly-traded enterprises or completed acquisition transactions involving similar companies.
The second step of the analysis relies upon the valuation provider’s economic model of the subject company’s capitalization structure. After determining the Enterprise Value of the overall company, the valuation provider must perform an Enterprise Value Allocation. This analysis attributes the overall Enterprise Value allocated to each class of shares in its capitalization structure. The most commonly-used valuation methods for this allocation are the Option Pricing Method (OPM) and the Probability-Weighted Expected Return Method (PWERM).
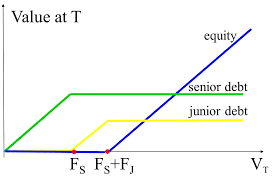
Explaining a Contingent Claims Model
To illustrate the value allocated to each class of shares, a valuation provider will create a Contingent Claims Model (CCM). This type of model considers the economic rights and preferences of the subject company’s securities. These include: preferred liquidation preferences, conversion points for preferred shares, exercise prices of granted options or warrants, and any additional features of the securities. If the subject company has significant financial leverage, the analysis will take into account the nature, amount, and term of the debt. Next, the valuation provider should consider management carve out plans and performance-vested options.
Contingent Claims Model analysis applies in the context of both the OPM and PWERM allocation models. CCM analysis will determine the value attributable to each class of securities in the capital structure. Last, valuation providers apply a Discount for Lack of Marketability (DLOM) to arrive at the FMV of the respective classes of shares. The IRS expects practitioners to calculate DLOM using one of several accepted Discount for Lack of Marketability quantitative models based upon option pricing theory.
What is the Process of Completing a 409A Valuation?
Many companies begin the process by identifying an independent valuation provider to complete the analysis and provide a report. They request recommendations from trusted advisors including board members, audit firms and corporate counsel. Key factors in selecting an appropriate valuation provider include:
- Extent of experience in serving similar companies (industry, stage, capital structure complexity)
- Total cost of service (including financial cost and management time commitment)
- Time to completion (availability and delivery commitment)
- Bedside manner (ability to interact with senior management, board members, and auditors)
After selecting a valuation service provider and signing an engagement agreement, management receives an Initial Information Request list. This request will include: company overview information, governance documents, details on capitalization, historical and projected financial statements, and information regarding historical investment transactions. Your valuation provider should acknowledge receipt of the information and revert with additional requests within 2-3 days.
Most valuation providers are capable of completing the analysis and providing it to management within 2-3 weeks. At Whitehawk Advisory we commit to deliver a draft of the valuation analysis within 10 business days of confirming information receipt. Next, the valuation provider will discuss the results with management. This conversation provides management with the opportunity to explain any differences in perspective on valuation or the assumptions used by the valuation provider. The engagement process time increases in proportion to the extent of external review and revisions to the draft work product.
Starting the Process with Whitehawk Advisory
Thanks for your time in reading through this summary of 409A valuation basics. For more information on our services in this area, please click here. We look forward to meeting you and seeing how we can help.



